Sacred Skin stands as a pioneering medical spa and esteemed skin care clinic within the vicinity of Johns Creek. Our establishment, Sacred Skin and Body, distinguishes itself by embodying the forefront of medical spa services and skin care practices. We are resolute in our commitment to offer an extensive range of progressive treatments and therapies. Our paramount objective is to enhance your innate beauty and foster your comprehensive well-being.
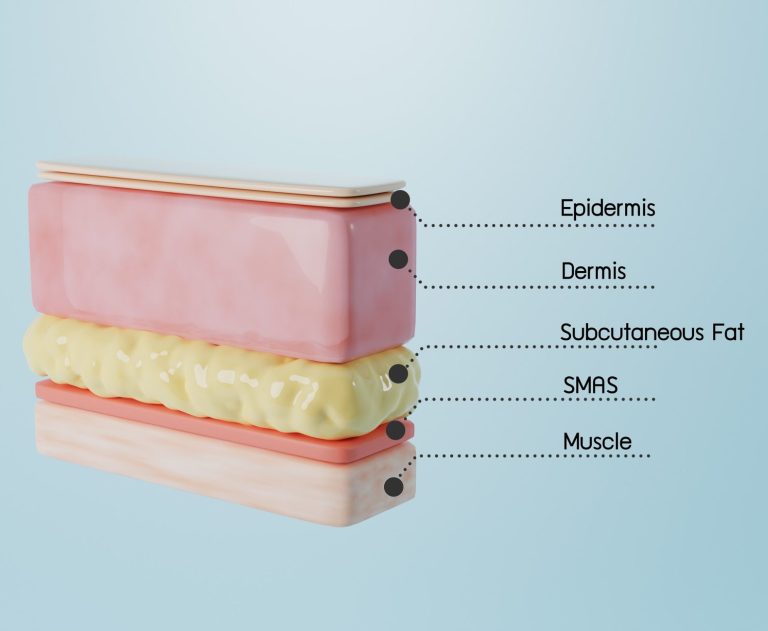
Hypodermis
(Subcutaneous Region)
Hypodermis - The region from the epidermis to the muscle is called the hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous tissue. It is the deepest layer of the skin and is made up of loose connective tissue and adipose tissue (fat cells). The hypodermis connects the skin to the underlying muscles and bones. It also provides insulation and protection for the body.
The hypodermis is an important part of the skin and plays a number of important roles, including:
- Insulation: The hypodermis helps to insulate the body by trapping heat. This helps to keep the body warm in cold weather.
- Protection: The hypodermis acts as a cushion, protecting the body from injury. The fat cells in the hypodermis also help to absorb shock.
- Energy storage: The adipose tissue in the hypodermis stores energy that can be used by the body when needed.
- Attachment: The hypodermis attaches the skin to the underlying muscles and bones.
The hypodermis is also involved in a number of other bodily functions, such as blood vessel regulation, immune function, and hormone production.
©Copyright 2023. All rights reserved.
